In the vast landscape of economic activities in the United States, there exists a rich tapestry of indigenous knowledge systems that have long been intertwined with the country’s history and development. While often overlooked or marginalized, these knowledge systems hold immense value, not only from a cultural and social perspective but also in terms of their contribution to secondary economic activities. In this blog, we delve into the significance of indigenous knowledge systems and how they play a vital role in shaping the secondary economy of the U.S.
Understanding Indigenous Knowledge Systems
Indigenous knowledge systems encompass a broad array of traditional practices, wisdom, and skills that have been passed down through generations within indigenous communities. These systems are deeply rooted in the land, environment, and cultural heritage of indigenous peoples, embodying a holistic understanding of the interconnectedness between humans, nature, and spirituality.
Preservation and Revitalization Efforts
Over the years, indigenous knowledge systems have faced threats of erasure due to colonialism, assimilation policies, and modernization. However, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of preserving and revitalizing these knowledge systems, both for the benefit of indigenous communities and the broader society.
Contributions to Secondary Economic Activities
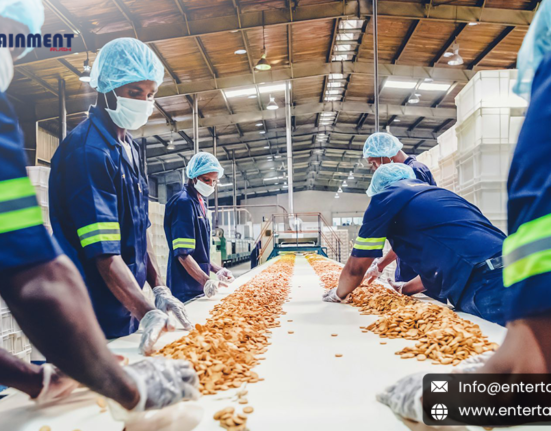
While indigenous knowledge systems are often associated with traditional livelihoods such as hunting, fishing, and agriculture, their influence extends far beyond primary economic activities. In the realm of secondary economic activities – which encompass manufacturing, processing, and services – indigenous knowledge systems offer unique insights, techniques, and practices that can enhance sustainability, innovation, and cultural authenticity.
Sustainable Resource Management
One of the key contributions of indigenous knowledge systems to secondary economic activities lies in sustainable resource management. Indigenous peoples have developed intricate systems of land stewardship, conservation, and resource utilization based on centuries of observation and adaptation to local ecosystems. By incorporating these traditional practices into modern industries such as forestry, agriculture, and tourism, there is potential to promote environmental sustainability while generating economic value.
Cultural and Artistic Heritage
Indigenous knowledge systems also play a significant role in shaping cultural and artistic expressions, which in turn contribute to secondary economic activities such as crafts, arts, and cultural tourism. Traditional crafts, music, storytelling, and visual arts not only provide avenues for cultural preservation and expression but also serve as sources of income and employment for indigenous communities.
Innovation and Adaptation
Far from being static or stagnant, indigenous knowledge systems are dynamic and adaptive, evolving in response to changing environmental, social, and economic conditions. In the realm of secondary economic activities, this adaptability fosters innovation and creativity, as indigenous communities leverage traditional knowledge to develop new products, services, and business models that are both culturally relevant and commercially viable.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their invaluable contributions, indigenous knowledge systems continue to face challenges such as cultural appropriation, intellectual property rights, and lack of recognition and support from mainstream institutions. However, there are also opportunities for collaboration, partnership, and knowledge exchange that can promote the integration of indigenous perspectives into broader economic frameworks. indigenous knowledge systems are not only repositories of traditional wisdom but also valuable resources for shaping the secondary economy of the United States. By recognizing, respecting, and integrating indigenous perspectives into economic activities, we can foster sustainability, cultural diversity, and inclusive development. Moving forward, it is essential to prioritize efforts to preserve, revitalize, and promote indigenous knowledge systems as integral components of the country’s economic and cultural heritage.




Leave feedback about this