The human body represents a marvel of biological engineering, where a sophisticated network of organs, tissues, and cells collaborates seamlessly to sustain life. To truly appreciate the capabilities of our bodies and effectively address health-related concerns, it is crucial to understand the structure and function of the human body. This exploration into anatomy and physiology sheds light on the intricacies of our bodies and reveals how they operate harmoniously.
Anatomy: The Study of Structure
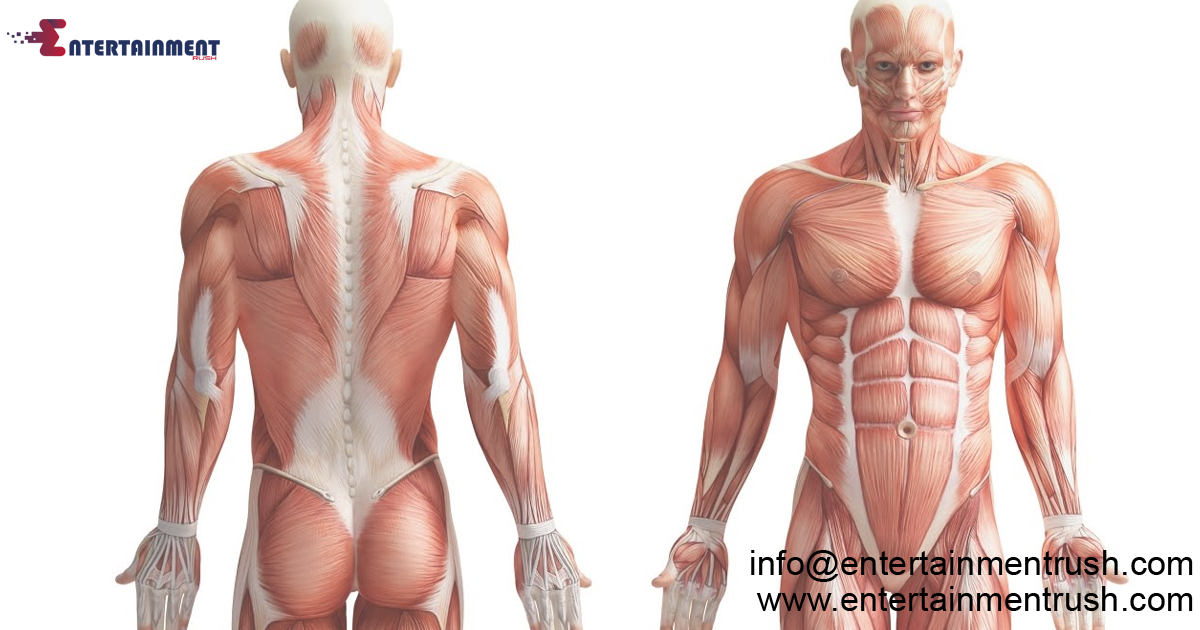
Anatomy is the discipline that delves into the physical structure of organisms, focusing on the relationships and interactions between various body parts. It involves a comprehensive examination of the shape, size, and organization of organs, tissues, and systems within the body. By studying anatomy, we gain a detailed map of the body’s architecture, enabling us to understand how its components integrate and function together.
Levels of Structural Organization
The human body is organized into distinct levels of structural complexity, each contributing to the overall functionality and coordination of bodily processes:
Cellular Level:
At the cellular scale, the body’s fundamental units are cells, each possessing specialized functions and structures essential for life.
Tissue Level:
Cells combine to form tissues, such as muscle, nerve, or connective tissue, each serving a specific purpose within the body.
Organ Level:
Organs are composed of different types of tissues organized to perform unique functions, exemplified by vital organs like the heart or lungs.
Organ System Level:
Organ systems, such as the cardiovascular or digestive system, comprise multiple organs working together synergistically to execute complex tasks critical for survival.
Physiology: The Study of Function
Physiology investigates how the body’s structures collaborate to sustain life and respond to environmental changes. It explores the intricate mechanisms that regulate bodily processes, including digestion, circulation, and sensory perception. By studying physiology, we gain insight into the dynamic nature of the human body, emphasizing its adaptability and resilience in maintaining homeostasis.
Key Physiological Processes
Physiology encompasses essential processes that sustain life and ensure optimal bodily function:
Homeostasis:
The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external fluctuations, crucial for health and survival.
Cellular Metabolism:
Intricate chemical processes within cells that produce energy and regulate vital functions essential for life.
Neural Communication:
Transmission of signals between nerve cells to coordinate bodily activities and respond to external stimuli.
Muscle Contraction:
Coordination of muscle fibers to generate movement and support bodily functions, facilitating mobility and strength.
Interdisciplinary Connections
Anatomy and physiology intersect with diverse scientific disciplines, enriching our understanding of health, disease, and human performance:
Medicine:
Medical professionals rely on anatomical and physiological knowledge to diagnose and treat illnesses effectively.
Research:
Biomedical research leverages anatomical and physiological insights to develop innovative therapies and technologies.
Sports Science:
Understanding the body’s mechanics enhances athletic performance optimization and injury prevention strategies.
Nutrition:
Knowledge of physiological processes informs dietary recommendations and promotes metabolic health.
The Human Body: A Symphony of Systems
The human body consists of several interconnected systems, each contributing unique roles and interactions critical for sustaining life:
Skeletal System:
Provides structural support and protection for vital organs and tissues, facilitating movement and mobility.
Muscular System:
Enables movement through muscle contraction and supports posture, essential for physical activity and functionality.
Nervous System:
Facilitates communication between body parts, coordinating responses to stimuli and regulating bodily functions.
Respiratory System:
Supplies oxygen to the blood and expels carbon dioxide from the body, supporting cellular respiration and metabolism.
Digestive System:
Processes food to extract nutrients and eliminate waste products, supporting growth, and energy production.
Cardiovascular System:
Circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing metabolic waste products. Anatomy and physiology serve as gateways to unraveling the intricate machinery of the human body. By exploring the complexities of structure and function, we gain profound insights into what makes us uniquely human. This knowledge not only informs medical practice and scientific discovery but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the wonders of our biology. As we continue to delve into the mysteries of anatomy and physiology, we unlock new avenues for improving health, enhancing performance, and unraveling the secrets of life itself. The journey into the human body is a captivating voyage, revealing the extraordinary capabilities that define our existence.



Leave feedback about this